Clothie E-commerce (Naba Hussam)
A custom e-commerce platform for a Pakistani fashion brand supporting both ready-to-wear and made-to-order products with local payment methods (COD, Bank Transfer), guest checkout with automatic account linking, and comprehensive admin management for orders, products, and settings
Problem
The Challenge
Context
A Pakistani fashion brand (Naba Hussam) required a custom e-commerce platform to sell women's clothing through two distinct business models: ready-to-wear (RTW) products with immediate fulfillment, and made-to-order (MTO) products with custom sizing and deposit-based payment plans. The platform needed to accommodate local payment preferences—specifically Cash on Delivery and Bank Transfer—while supporting guest checkout for reduced friction and automatic account linking for order history preservation.
User Pain Points
Need to support both ready-to-wear and custom made-to-order products with different fulfillment workflows
Local payment methods (COD, Bank Transfer) required for Pakistani market where credit cards are not widely adopted
Managing dynamic product categories and subcategories for different clothing types
Supporting guest checkout while allowing account creation for order history preservation
Providing size guidance for custom orders through uploadable size charts
Handling regional shipping options with different delivery charges (within/outside Karachi)
No mechanism for guest-to-authenticated user order linking in existing solutions
Why Existing Solutions Failed
Generic e-commerce platforms failed to address specific requirements: no native support for made-to-order workflows with deposit payments and modification deadlines, international payment gateways created friction for local customers, limited customization for regional shipping zones, and no built-in support for product add-ons like additional clothing pieces.
Goals & Metrics
What We Set Out to Achieve
Objectives
- 01Build a complete e-commerce platform supporting both RTW and MTO products with distinct checkout flows
- 02Implement COD and Bank Transfer payment methods tailored for local market preferences
- 03Create admin panel for comprehensive product, order, and settings management
- 04Support guest checkout with automatic order linking when accounts are created
- 05Enable dynamic category/subcategory management with MTO/RTW type assignment
- 06Integrate AWS S3 for reliable image storage with aspect ratio validation
- 07Implement GA4-compatible event tracking for e-commerce analytics
- 08Deploy via Docker with Nginx reverse proxy for production security
Success Metrics
- 01Successful order placement through both COD and Bank Transfer payment methods
- 02Admin ability to manage entire product catalog without developer intervention
- 03Guest users can complete checkout without registration
- 04Products correctly categorized as MTO or RTW with appropriate checkout enforcement
- 05Images reliably stored and served from S3 with consistent 2:3 aspect ratio
- 06Analytics events firing correctly for view_item, add_to_cart, and purchase tracking
- 07COD orders trackable with delivery service assignment and attempt logging
- 08MTO orders include deposit/balance tracking with modification deadlines
User Flow
User Journey
The system handles the complete e-commerce customer journey: browsing products by category, viewing product details with size options and add-ons, managing cart with size-specific quantities, proceeding through checkout with payment method selection based on product type, and order confirmation with analytics tracking.
Architecture
System Design
Modular monolith architecture with two separate React frontend applications (Customer SPA + Admin Dashboard) connected to a unified Express backend API. The backend handles authentication, product management, orders, and cart operations while integrating with MongoDB Atlas for data persistence and AWS S3 for image storage.
What This Diagram Represents
The complete system topology showing all applications, services, external dependencies, and network boundaries. This diagram illustrates how two separate frontend applications (Customer SPA and Admin Dashboard) communicate with a centralized Express backend, which interacts with MongoDB for data persistence and AWS S3 for image storage.
How to Read the Flow
Key Engineering Decisions
Layer Breakdown
Frontend Layer
Backend Layer
Data Layer
External Integrations
Security
Authentication Flow
JWT-based authentication with separate customer and admin flows, plus automatic guest order linking on account registration.
What This Diagram Represents
The complete authentication lifecycle for both customers and admins, including the unique guest order linking mechanism that automatically associates guest orders when users create accounts.
How to Read the Flow
Key Engineering Decisions
Customer Authentication
- •Email/password login with bcrypt verification
- •JWT tokens stored in localStorage
- •Guest checkout with email-based order tracking
- •Automatic order linking on registration
Admin Authentication
- •Dual system: DB admins + environment fallback
- •Admin JWT includes isAdmin flag
- •Separate adminAuth middleware for protected routes
- •No access to customer endpoints from admin tokens
Checkout Flow
Order Lifecycle
End-to-end order placement from cart review to confirmation, with intelligent payment method routing for different product types.
What This Diagram Represents
The end-to-end order placement flow from cart review to order confirmation, showing payment method routing, server-side validation, and the divergent paths for COD versus Bank Transfer orders.
How to Read the Flow
Key Engineering Decisions
Cash on Delivery (COD)
- •Available for Ready-to-Wear (RTW) products only
- •COD details subdocument for delivery tracking
- •Delivery service assignment and attempt logging
- •Collection verification by admin
Bank Transfer
- •Required for Made-to-Order (MTO) products
- •Bank details displayed from settings
- •Optional payment proof upload to S3
- •Admin verification before processing
Data Pipeline
Product Data Flow
Complete product lifecycle from admin creation through S3 image storage to customer display, including search functionality.
What This Diagram Represents
The complete product lifecycle from admin creation through S3 upload to customer display, including the image validation pipeline and search functionality.
How to Read the Flow
Key Engineering Decisions
Image Validation
Client-side 2:3 aspect ratio validation ensures consistent product grid display before upload begins.
S3 Storage
Images uploaded via Multer memory buffer to AWS S3. Public URLs served directly without backend proxying.
Debounced Search
300ms debounce reduces API calls. Regex query matches product name, category, and subcategory fields.
State Management
Shopping Cart
Cart state synchronization between client, server, and storage with seamless merge logic when guest users create accounts.
What This Diagram Represents
Cart state synchronization between client, server, and storage for both guest and authenticated users, including the cart merge logic that runs on login.
How to Read the Flow
Key Engineering Decisions
Cart Data Structure
// Nested object for O(1) lookups
cartData = {
"product_id_1": {
"M": 2, // Size M, qty 2
"L": 1 // Size L, qty 1
},
"product_id_2": {
"S": 3 // Size S, qty 3
}
}Add-ons Structure
// Separate state avoids deep nesting
cartAddOns = {
"product_id_1": [
{ name: "Dupatta", price: 500 },
{ name: "Trouser", price: 800 }
]
}Guest Users
Cart stored in localStorage only. Zero backend calls until checkout.
Authenticated
Cart synced to MongoDB via user.cartData field. Persists across devices.
Cart Merge
Additive merge on login. Guest M:2 + DB M:1 = Result M:3. No data loss.
Custom Orders
Made-to-Order Workflow
Specialized workflow for custom products including design selection, deposit payments, modification windows, and production tracking.
What This Diagram Represents
The specialized workflow for Made-to-Order products including custom sizing, deposit payments, modification windows, and production tracking phases.
How to Read the Flow
Key Engineering Decisions
MTO Order Lifecycle Phases
Selection
- • Choose design category
- • Select custom size
- • View MTO size chart
- • Add to cart
Checkout
- • Bank Transfer enforced
- • Deposit calculated
- • Payment proof optional
- • Order submitted
Modification
- • Deposit verified
- • Change window opens
- • Design adjustments
- • Deadline locks design
Production
- • Production starts
- • Balance reminder
- • Payment verified
- • Ready for delivery
MTO vs RTW Product Comparison
| Aspect | Made-to-Order (MTO) | Ready-to-Wear (RTW) |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Methods | Bank Transfer only | COD or Bank Transfer |
| Payment Structure | Deposit + Balance (two-stage) | Full payment at delivery |
| Sizing | Custom sizes from MTO chart | Standard sizes (S, M, L, XL) |
| Modifications | Within deadline window | Not applicable |
| Fulfillment | After production (days/weeks) | Immediate from inventory |
Data Flow
How Data Moves
Data flows through the system starting from user interactions on the frontend, through authenticated API requests to the Express backend, which orchestrates MongoDB operations for data persistence and S3 operations for image storage. Responses are returned as JSON with consistent success/error patterns.
Core Features
Key Functionality
Dual Product Type System (MTO + RTW)
What it does
Supports both immediate-fulfillment ready-to-wear products and custom made-to-order products with different pricing, sizing, and payment structures
Why it matters
Enables the brand to serve both quick-purchase customers and those wanting custom-tailored garments from a single platform
Implementation
Products flagged with isMakeToOrder and productType fields. MTO products have additional mtoAttributes for design categories, custom sizes, and production time. Checkout enforces Bank Transfer for MTO items.
Shopping Cart with Size-Specific Quantities
What it does
Tracks cart items with granular size/quantity tracking using nested object structure {itemId: {size: qty}} plus separate add-ons tracking
Why it matters
Allows customers to order multiple sizes of the same product (e.g., M:2, L:1) and optional add-ons like dupatta, all in one checkout
Implementation
Cart stored as nested object enabling O(1) lookups. Authenticated users sync to user.cartData in MongoDB. Guests use localStorage. Carts merge additively on login.
Guest Checkout with Account Linking
What it does
Allows order placement without authentication using email, automatically links orders when accounts are created with the same email
Why it matters
Reduces checkout friction for new customers while preserving order history capability when they decide to create accounts
Implementation
Guest orders stored with guestEmail and isGuestOrder flag. On registration, linkGuestOrders() queries by email and bulk-updates orders to new userId.
COD Management System
What it does
Full lifecycle management for Cash on Delivery orders including delivery service assignment, attempt tracking, and collection verification
Why it matters
COD is the dominant payment method in Pakistan. System provides admin visibility into delivery status and payment collection
Implementation
Order model includes codDetails subdocument with deliveryService, trackingId, deliveryAttempts array, and collection status fields.
Dynamic Category Hierarchy
What it does
Admin-managed category structure supporting subcategories and product type (MTO/RTW) assignment for filtering and navigation
Why it matters
Enables the brand to reorganize product catalog without developer intervention as collections change seasonally
Implementation
productCategoryTree stored in settings as array of objects with name, type, and subs array. Frontend reads from centralized settings.
S3 Image Management
What it does
Handles product image uploads with client-side 2:3 aspect ratio validation and public URL generation
Why it matters
Ensures consistent product grid display and offloads image serving to S3 CDN infrastructure
Implementation
Frontend validates ratio using Image object. Multer uses memory storage. S3 client uploads with unique keys. Public URLs constructed from bucket/region/key pattern.
Product Add-ons System
What it does
Allows products to have optional purchasable additions (e.g., dupatta, trouser) with per-item pricing tracked separately in cart
Why it matters
Traditional Pakistani clothing often includes optional pieces. System enables upselling while maintaining accurate pricing
Implementation
Products have addOns array with name/price objects. Frontend renders checkboxes, tracks in cartAddOns state. Order totals include add-on prices.
E-commerce Analytics Tracking
What it does
Fires GA4-compatible events for view_item, add_to_cart, remove_from_cart, begin_checkout, and purchase with proper e-commerce schema
Why it matters
Enables data-driven decision making through Google Analytics and Tag Manager integration
Implementation
Events pushed to dataLayer for GTM and directly to gtag. Includes currency (PKR), value, and items array with item_id, item_name, price, quantity.
Technical Challenges
Problems We Solved
Why This Was Hard
MTO products require Bank Transfer deposits, while RTW allows COD. Cart can contain mixed items, but payment method applies to entire order. Cannot split orders by product type due to business constraints.
Our Solution
Payment validation at both UI (UX) and API (security) layers. Frontend checks for MTO items and disables COD option. Backend rejects COD if any item is MTO. Mixed cart warning informs users that Bank Transfer will apply to entire order.
Why This Was Hard
User adds items as guest (localStorage), then logs in with existing cart in database. Must merge without losing guest selections, handling size conflicts (different quantities for same product/size).
Our Solution
Additive merge logic: dbCart + localCart. Size M:2 (guest) + M:1 (db) = M:3 result. Merged cart synced back to backend, localStorage cleared. Prevents data loss from any browsing session.
Why This Was Hard
Link guest orders to new accounts using email, but no email verification exists. Risk: User A places guest order, User B registers with same email first, gains access to orders.
Our Solution
First-come-first-served email registration. Risk deemed acceptable for MVP. Email verification prioritized for future release. Security trade-off documented explicitly.
Why This Was Hard
Product grid displays images in 2:3 aspect ratio cards. Inconsistent ratios break layout. Backend cannot validate dimensions without decoding buffer. Server-side processing adds latency.
Our Solution
Client-side validation before upload using Image object. Validates ratio before sending to server (fail-fast). No server-side enforcement (API can be bypassed). Future enhancement: Sharp.js for server resize/crop.
Why This Was Hard
Categories referenced by name strings across product documents, navigation, and filters. Category rename requires updating all products. No referential integrity.
Our Solution
Single source of truth in settings document. String-based references acceptable for slowly-changing dimensions with low cardinality. Category changes are rare in practice. Client-side validation only.
Why This Was Hard
Need delivery tracking for COD orders without API integrations for local delivery services (TCS, Leopards, local riders). No standardized API exists.
Our Solution
Flexible codDetails subdocument with free-text delivery service field, manual tracking ID entry, and delivery attempts array. Admin workflow: assign service, enter tracking, log attempts, mark collected.
Engineering Excellence
Performance, Security & Resilience
Performance
- Products fetched once on app load and cached in React Context, eliminating repeated API calls during navigation
- Search input debounced at 300ms to reduce API calls from ~10/second to ~3/second during typing
- Cart persisted in localStorage for guests reducing server roundtrips to zero until checkout
- S3 images served directly without server proxying, leveraging S3 CDN infrastructure
- Promise.all for parallel image uploads (4 images in ~2s vs ~8s sequential)
- Mongoose .select() for selective field projection retrieving only needed fields
Error Handling
- Global Multer error middleware catches file size, file count, and unexpected field errors
- Consistent JSON response pattern with success boolean across all endpoints
- Try-catch blocks in all controller functions with error.message in response
- Frontend toast notifications provide immediate error feedback to users
- S3 upload failures caught and re-thrown with context for debugging
- MongoDB ObjectId format validation on product pages prevents invalid queries
- Empty cart validation prevents order placement attempts with no items
Security
- JWT token-based authentication for protected routes with token in headers
- bcrypt password hashing with 10 salt rounds meeting OWASP recommendations
- CORS configured with explicit origin whitelist (nabahussam.com, admin.nabahussam.com)
- Backend binds to localhost only (127.0.0.1:7000), accessible only via Nginx reverse proxy
- Separate adminAuth middleware validates isAdmin flag in JWT for admin routes
- File upload restrictions: 20MB size limit and image mimetype validation via Multer
- Input validation using validator.js library for email format and password length
Design Decisions
Visual & UX Choices
Separate Frontend Applications
Rationale
Customer and admin UIs deployed independently for security isolation and independent scaling. Admin dashboard never exposed to customer traffic.
Details
Two React SPAs on different subdomains (nabahussam.com, admin.nabahussam.com). Each bundles only code needed for that role. Nginx routes requests based on subdomain.
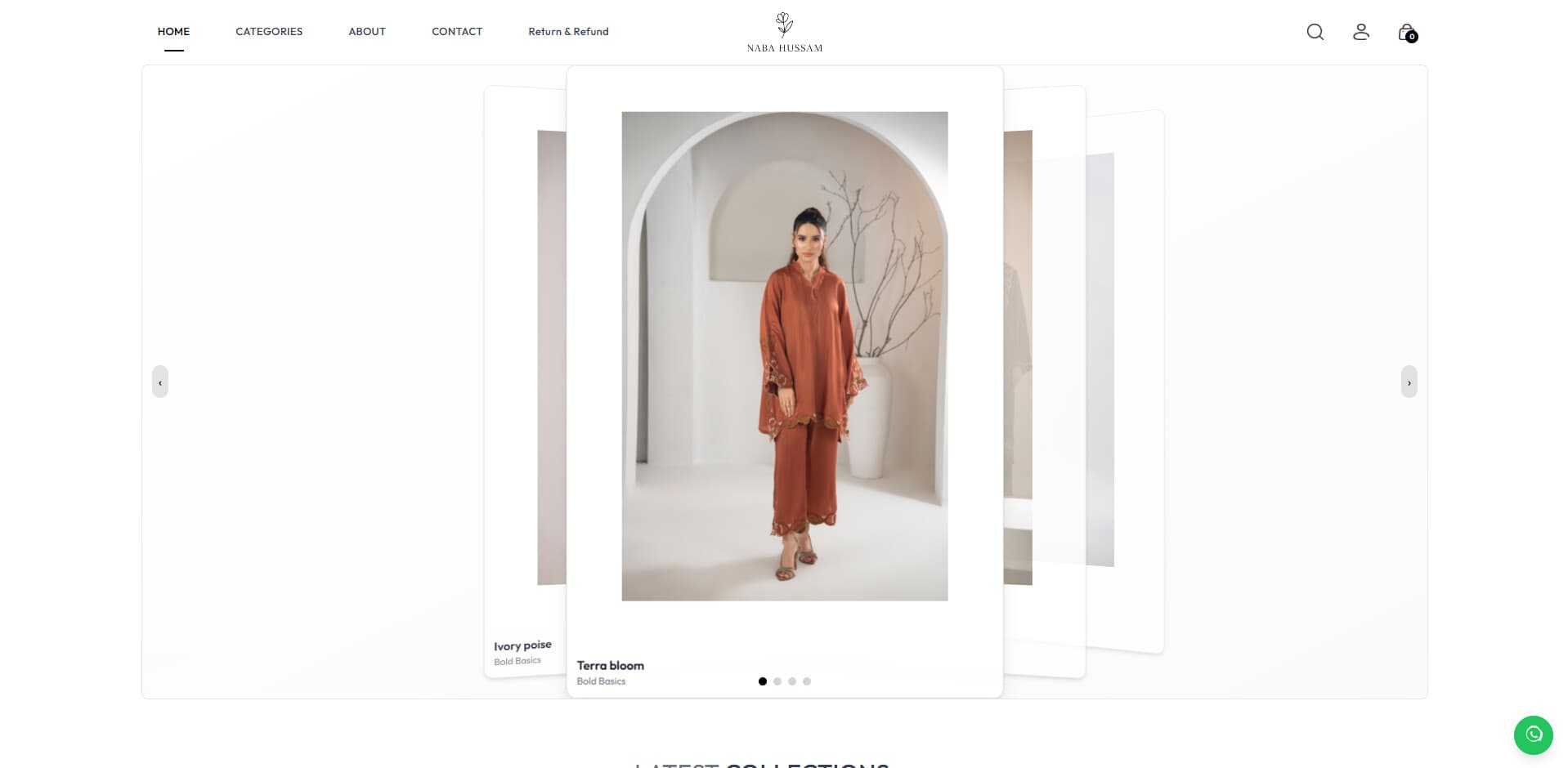
Card-Based Product Grid
Rationale
Consistent 2:3 aspect ratio cards create visual harmony. Hover effects provide interaction feedback without overwhelming the browsing experience.
Details
ProductItem components with image zoom on hover. Loading skeleton during image fetch. Price formatted with PKR currency. Bestseller badge for featured items.
Slide-In Cart Drawer
Rationale
Keeps users in context without full page navigation. Quick cart access improves purchase flow by showing immediate feedback on add-to-cart actions.
Details
CartDrawer component slides from right. Shows items with size/quantity breakdown. Add-ons listed separately. Real-time total calculation. Checkout button prominently placed.
Modal-Based Size Charts
Rationale
Size guidance critical for custom MTO orders. Modal keeps users on product page while providing detailed measurements.
Details
Separate size charts for MTO and RTW products uploaded by admin to S3. Fetched from settings.sizeCharts. Full-screen modal with close button.
Status-Colored Order Badges
Rationale
Visual distinction between order states enables quick scanning in admin dashboard. Color coding follows established UX patterns.
Details
Pending = yellow, Processing = blue, Shipped = purple, Delivered = green, Cancelled = red. Badges used consistently across order list and detail views.
Impact
The Result
What We Achieved
Successfully deployed complete e-commerce platform with product catalog, cart, and checkout supporting both COD and Bank Transfer payments. Admin dashboard enables full product and order management. Guest checkout with automatic account linking implemented. Dynamic category management with MTO/RTW support operational. S3-based image storage with reliable delivery. GA4-compatible analytics event tracking implemented. Production deployment via Docker with Nginx reverse proxy.
Who It Helped
Brand owner gained ability to manage entire product catalog, process orders, and configure settings without developer intervention. Customers can browse products, use guest checkout with reduced friction, and have orders automatically linked when creating accounts. Admin staff can track COD deliveries, verify bank transfers, and manage MTO orders with deposit/balance tracking.
Why It Matters
Demonstrates ability to build custom e-commerce solutions tailored to specific market requirements (Pakistani payment preferences, dual product types, regional shipping). Shows full-stack capability from React frontend to Express backend to cloud deployment. Addresses real business needs rather than generic solutions.
Reflections
Key Learnings
Technical Learnings
- S3 direct URLs with proper bucket policies eliminate need for signed URLs for public product images
- Multer memory storage simplifies deployment but requires memory awareness for concurrent uploads
- DataLayer-based analytics tracking provides flexibility for different analytics tools (GA4, GTM)
- Nested object structure for cart enables O(1) lookups but requires careful merge logic
- Client-side validation improves UX but must be duplicated server-side for security
- JWT tokens without expiration create security risk - future enhancement needed
Architectural Insights
- Modular monolith with separate frontend apps balances deployment flexibility with codebase simplicity
- Centralized settings document simplifies cross-feature configuration (bank details, shipping, categories)
- Guest checkout with email linking provides flexibility without separate guest user documents
- Product type flags (MTO/RTW) enable differentiated checkout logic without separate product models
- COD details as subdocument keeps order model cohesive while supporting complex tracking
- Docker with Nginx reverse proxy provides secure production deployment pattern with localhost binding
What I'd Improve
- Add JWT token expiration with refresh token mechanism for improved security
- Implement rate limiting on API endpoints to prevent brute force attacks
- Add email verification on registration to secure guest order linking
- Implement server-side image processing with Sharp.js for guaranteed aspect ratios
- Add database indexing strategy for better query performance at scale
- Consider Redis caching layer for frequently accessed settings and products
Roadmap
Future Enhancements
Enable email notifications for order confirmations and status updates
Implement password reset flow with email-based reset tokens
Add inventory management with stock tracking and out-of-stock indicators
Enable Stripe/Razorpay for online payments (already integrated, currently disabled)
Implement rate limiting for API protection (express-rate-limit)
Add JWT token expiration and refresh mechanism (currently no expiration)
Implement product reviews and ratings (schema exists, code commented out)
Add admin analytics dashboard with sales reports and metrics
Implement bulk product operations (CSV import/export)
Add CloudFront CDN for S3 images to improve global load times
Implement server-side pagination for large product catalogs
Add wishlist functionality for customers